Regulatory trends influencing international cross-border transport
Regulatory developments are reshaping how vehicles and fleets operate across borders, affecting everything from electrification and charging networks to vehicle autonomy and emissions controls. Policymakers, operators, and infrastructure providers are adjusting standards to balance safety, interoperability, and environmental goals while addressing practical issues such as battery range and maintenance requirements.

How does electrification and charging affect cross-border routes?
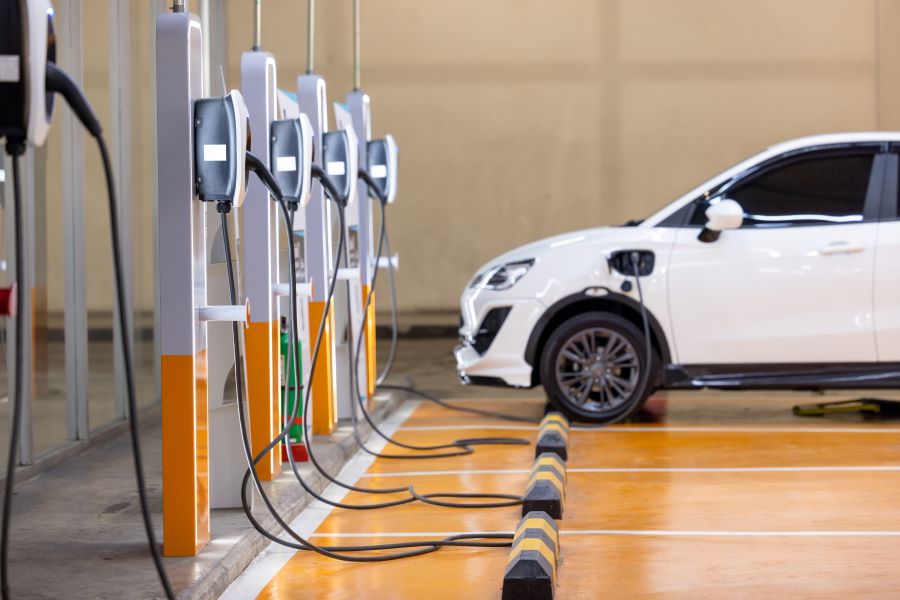
Electric vehicle electrification is central to cross-border transport policy. Regulations increasingly focus on harmonizing charging standards, payment interoperability and safety protocols to avoid fragmentation at borders. Differences in connector types, roaming agreements for charging networks, and rules for high-power charging stations can create operational friction for international fleets. Regulators are working to align technical standards and require transparent information about charging availability and power levels so vehicles can reliably plan routes without incurring long detours or service interruptions.
What infrastructure and connectivity challenges do regulators address?
Infrastructure policy now integrates road, energy and digital connectivity concerns. Cross-border corridors require consistent rules for grid upgrades, roadside power supply, and data exchange between transport authorities. Connectivity standards for telematics and fleet management systems are being introduced to ensure regulatory data — such as vehicle weight, emissions status and driver logs — can be shared securely across jurisdictions. Regulations increasingly mandate open data interfaces and cybersecurity measures to protect systems while enabling navigation and route optimization tools to access timely information.
How do battery, range and maintenance rules interact with regulation?
Battery certification and vehicle range declarations are becoming part of cross-border compliance regimes. Authorities are proposing clearer labeling of battery capacity and standardized test procedures so range claims are comparable between markets. Maintenance regulations focus on safety-critical elements linked to electrification, such as high-voltage systems, battery cooling and state-of-health monitoring. Cross-border operators must account for different inspection regimes and technician qualification requirements, prompting both harmonized training standards for maintenance personnel and recognition of certified service centers in neighboring countries.
How are emissions and safety standards harmonized internationally?
Emissions regulation remains a major driver for international policy alignment, with many jurisdictions tightening limits and introducing zero-emission zones that can affect routing for long-haul transport. Safety standards for vehicles — including crash testing, electronic stability systems and emergency response protocols for battery incidents — are being updated to reflect new powertrain technologies. Harmonization efforts often focus on mutual recognition of type approvals and uniform reporting of emissions to reduce administrative burdens and ensure consistent enforcement while maintaining road safety.
What rules govern autonomy and navigation across borders?
Autonomy introduces complex regulatory questions for cross-border travel: liability, software updates, data privacy and minimum performance standards for automated driving functions. Regulators are exploring frameworks for certifying autonomous systems that can operate under multiple national rules, and for enabling reliable navigation when switching between local digital maps or differing traffic regulations. Requirements for fail-safe behavior, human-machine interface standards, and secure connectivity are emphasized so that autonomous or connected vehicles navigate consistently and safely across different legal regimes.
How do fleet rules, connectivity and cross-border compliance work together?
Fleet operators face overlapping requirements: driver hours, vehicle certification, emissions reporting, and digital record-keeping. Regulators are increasingly mandating telematic systems that capture compliance data and enable authorities to audit cross-border movements. Connectivity mandates and standardized electronic documents help streamline customs and border checks, while common rules for driver training and vehicle maintenance reduce operational complexity. Insurance and liability frameworks are also under review to address multi-jurisdictional incidents involving connected or electrified vehicles.
Conclusion
Regulatory trends affecting international cross-border transport aim to balance environmental objectives, safety, and operational continuity. Progress toward harmonized standards for electrification, charging, battery information, connectivity, emissions and autonomous functions can reduce friction for cross-border fleets and improve predictability. Continued coordination among regulators, industry and infrastructure providers will be important to translate policy into practical, interoperable systems that support long-distance mobility and trade.